What Is HVAC and How Does It Work? (Full Guide)

Your HVAC system impacts your comfort, health, and energy bills. But do you really know what is HVAC system in a building? Do you know about the way it functions, the components it has, its types, or the cost range for repairing or installing it?
This is your A-to-Z guide on HVAC systems and everything you should know about them. Let’s start with what is HVAC.
What Does HVAC Stand for?
First things first, what is HVAC? HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. HVAC isn’t a simple unit. In fact, it includes various parts to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality within a building.
What Does HVAC Mean?
As mentioned, HVAC is an acronym for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. This system provides (and maintains) comfortable, healthy indoor environments by controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality.
What Are the Main Components of an HVAC System?
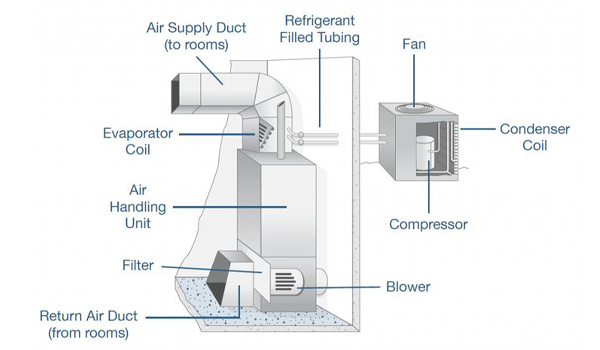
Now that we’ve cleared what is HVAC system in the building, let’s see what its components are. The main parts include the main unit, furnace, thermostat, (de)humidifier, air handler, evaporator coil, etc.
Let’s have a closer look:
The Main Unit
The main unit is the core component responsible for either heating or cooling the air. Examples of main units include air conditioners, which cool indoor air by removing heat and moisture; chillers, which provide chilled water for air conditioning systems; and heat pumps, which can both heat and cool by transferring heat from one place to another.
Furnace
The furnace is a heating component that generates heat using fuel or electricity, distributing warm air through the duct system. Find out more about furnace inspection in our previous blog.
Thermostat
The thermostat is a control device that allows you to set and monitor your preferred temperature. It regulates the system by signaling when to heat or cool the air. That’s why they call it the “brain” of HVAC systems.
Humidifier/Dehumidifier
These components manage indoor humidity levels. The humidifier adds moisture to the air to enhance dry conditions, while the dehumidifier removes excess moisture to improve air quality and prevent mold.
Air Handler
The air handler circulates air through the system. It had a blower, heating/cooling elements, and filters to ensure efficient air flow and quality.
Evaporator Coil
The evaporator coil is inside the air handler. It absorbs heat from the indoor air, allowing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the air before it circulates back into the building.
Condenser Coil
The condenser coil is in the unit outside the building. This coil releases the heat absorbed from the indoor air, condenses the refrigerant back into liquid form, and prepares it for another cooling cycle.
Ductwork
In an HVAC system, ductwork is a network of ducts that transports heated or cooled air to different areas of the building. It should be designed and installed properly to ensure efficient airflow and temperature regulation.
Heat Exchanger
You may have heard about heat exchangers in thermal inspection as they are found in furnaces and heat pumps. Heat exchangers transfer refrigerant or heat (from the combustion process) to the air circulating in the home, ensuring effective heating and cooling.
All these components will be evaluated during a dedicated assessment, find out more here: what is HVAC inspection?
What Are Different Types of HVAC Systems?
HVAC systems can be ducted or ductless, and their most common types include:
Split HVAC System
A split system has two main units: an indoor unit (air handler or furnace) and an outdoor unit (condenser or compressor). The indoor unit circulates air throughout the building, and the outdoor unit extracts heat from the refrigerant.
This system can provide heating/cooling for residential and commercial spaces, especially where central air conditioning is needed
Packaged HVAC System
A packaged HVAC system combines all the heating and cooling components into a single unit. Therefore, it uses a single unit to manage both heating and cooling by drawing air from inside the building, conditioning it, and then redistributing it.
Packaged systems are commonly found in commercial settings where space is limited too. They’re typically installed on the roof or a concrete slab next to the building.
Ductless Mini-Split System
These systems consist of an outdoor compressor unit and one or more indoor air handling units. They provide direct and independently controlled cooling/heating for each room without ductwork.
Because of this, they’re ideal for residential spaces, especially in homes without existing ducts, as well as for room additions and renovations.
Central HVAC System
Central systems use a centralized location to heat or cool air. They have a furnace or air conditioner to condition the air and then deliver it through ducts to different rooms. They can also have a thermostat for temperature control.
Central HVACs are suitable for large homes and commercial buildings that require efficient air distribution.
VRF HVAC System
A VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) system utilizes refrigerant as the cooling/heating medium, connecting multiple indoor units to a single outdoor unit. It adjusts the flow of refrigerant to each indoor unit based on specific settings and provides simultaneous heating and cooling in different zones.
VRF systems are perfect for large commercial buildings and multi-family residential units since they offer seamless flexibility and efficiency.
Hybrid HVAC System
A hybrid HVAC system combines a traditional heating and cooling system with a heat pump for energy efficiency. Based on outside temperatures, it automatically selects the most efficient heating method (heat pump or furnace).
Hybrid systems are effective for both residential and commercial buildings in regions with varied climate conditions.
How Do HVAC Systems Work?
When you change the temperature, the thermostat signals the system to heat or cool the air. The furnace or heat pump generates heat, or the air conditioner removes heat. Then the air is circulated through the building via ducts or directly from indoor units (in ductless systems).
Ventilation using exhaust fans or air purifiers is also crucial to exchange indoor air with fresh outdoor air and maintain air quality. For a more detailed explanation, check out this video.
How Much Does a New HVAC System Cost?
The cost of a new HVAC system varies based on the type of system, its capacity, and installation complexity. Let’s have a general overview of the prices:
HVAC Systems Repair Costs
HVAC repair costs vary widely depending on the system’s type and age, the nature of the problem, and the region you're in. Here's an overview of typical HVAC repair costs in Canada:
Also read: How much does a furnace inspection cost?
Conclusion
When talking about what is HVAC, it always goes beyond simply heating and cooling. This system plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of occupants in a building. By understanding its function and proper maintenance, you’ll enjoy more comfort and an increased quality of life and/or work.
- In this post:
- What Does HVAC Stand for?
- What Does HVAC Mean?
- What Are the Main Components of an HVAC System?
- What Are Different Types of HVAC Systems?
- How Do HVAC Systems Work?
- How Much Does a New HVAC System Cost?
- HVAC Systems Repair Costs
- Conclusion



